Remove Kinsearch browser hijacker virus from your computer by reading my virus removal guide.
First and foremost, let’s find out what Kinsearch is before we can discuss how to remove it. Further knowledge of this threat will aid you in recognizing similar threats quickly in the future.
By taking a closer look at it, it becomes apparent that Kinsearch is more than just a mere browser tool; it is a browser hijacker. This means that everytime you open your internet browser, it secretly compels you to visit a specific website (Kinsearch).
This happens after it has been installed by slyly modifying your web browser’s settings.
The sneaky thing about Kinsearch is how it gets onto your PC. Sometimes, people unknowingly add this software as they might think that their browsing experience could be better or when it comes bundled with other programs so they do not see any harm in installing them. Once installed however, such programs change your search results and home pages which now point to the Kinsearch without your consent.
What makes this even annoying is that while trying to go back to your usual sites, you still keep ending up on this hijacker instead. That’s not just inconvenient; also remember that there are privacy issues associated with spammers who always track users’ online activities.
What exactly is Kinsearch?
Positioning itself as an easy-to-use homepage option for users looking for smooth browsing experiences, Kinsearch is not what it claims to be on the surface. This software operates as a browser hijacker at its core.
When we say browser hijackers modify settings within your web browser without receiving permission from the user, one of clear indications of their influence can tell when they change the default search engine and take over any new tabs’ homepages, redirecting them to their own site — in this case: Kinsearch.
Kinsearch browser hijacker
Summary:
- Kinsearch presents itself as a handy homepage option and search tool.
- It claims to offer seamless browsing experiences to users.
- It is a browser hijacker.
- It modifies settings within your web browser without permission.
- It alters the default search engine and takes over the new tab’s homepage.
- It redirects the homepage to its page.
Kinsearch domain WHOIS record:
We were unable to provide WHOIS data on this domain.
Kinsearch domain age:
We were unable to provide WHOIS data on this domain.
Why is Kinsearch Harmful?
Although Kinsearch might initially appear harmless or useful, it conceals its primary intent: data collection. The browser hijacker is designed to gather various data from your web activities. This could range from your search histories, visited websites, and interactions on specific sites to personal data like location, IP address, and more.
The data amassed by Kinsearch isn’t merely stored; it’s actively monetized. It is often sold to advertising networks, thereby allowing tailored ads to be shown to you, often in an intrusive manner. The barrage of targeted ads isn’t just annoying; it can slow browsing and expose you to potential threats.
Additionally, because Kinsearch extracts data without users’ explicit consent, it’s tagged as a potentially unwanted program (PUP). The PUP classification is reserved for programs that might not be malicious, like viruses, but can pose risks or annoyances to the user.
Summary:
- Kinsearch is a browser hijacker that collects data from users’ web activities
- It collects information such as search histories, visited websites, and personal data like location and IP address
- The collected data is monetized and sold to advertising networks for targeted ads
- This can lead to annoying and intrusive ads, as well as potential browsing issues and security threats
- Kinsearch is considered a potentially unwanted program (PUP) because it extracts data without explicit user consent
How Does Kinsearch Spread?
Even though Kinsearch might seem harmless or beneficial at first sight, it masks its major purpose – to collect data. Most often, browser hijackers extract all possible information from your web activities.
It can include the search history, visited pages and actions in some websites to personal data like our location and IP address.
The collected information by Kinsearch is not just stored; it is actively monetized. By selling these data to advertisement networks, you are able to see personalized ads most times annoyingly popping up on your device. The incessantness of directed advertisements does not only bother; but likewise slows down the internet while exposing you to threats.
Additionally, as Kinsearch takes hold of users’ data without their explicit permission it classifies it as potentially unwanted program (PUP). However, PUPs are programs that may not be harmful like viruses but may pose risks or annoyances to a user.
Summary:
- Kinsearch is a browser hijacker that captures user’s online activity
- It gathers such information as search histories, visited sites and also individuals’ private details like places of residence and IP addresses
- The information gathered is commercialized through selling them advertising agencies hence leading to targeted ads
- These are irritating and intrusive ads that can result in browsing issues as well as security threats
Remove Kinsearch from Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Firefox
Remove the Extension via Chrome:
- Go to
chrome://extensionsand try to delete the extension there.
Extensions with Enterprise Policy:
Some extensions may have an “enterprise policy” preventing deletion. In this case, try the following steps before proceeding to the Last Resort methods below:
1. Reset browser to Default Settings:
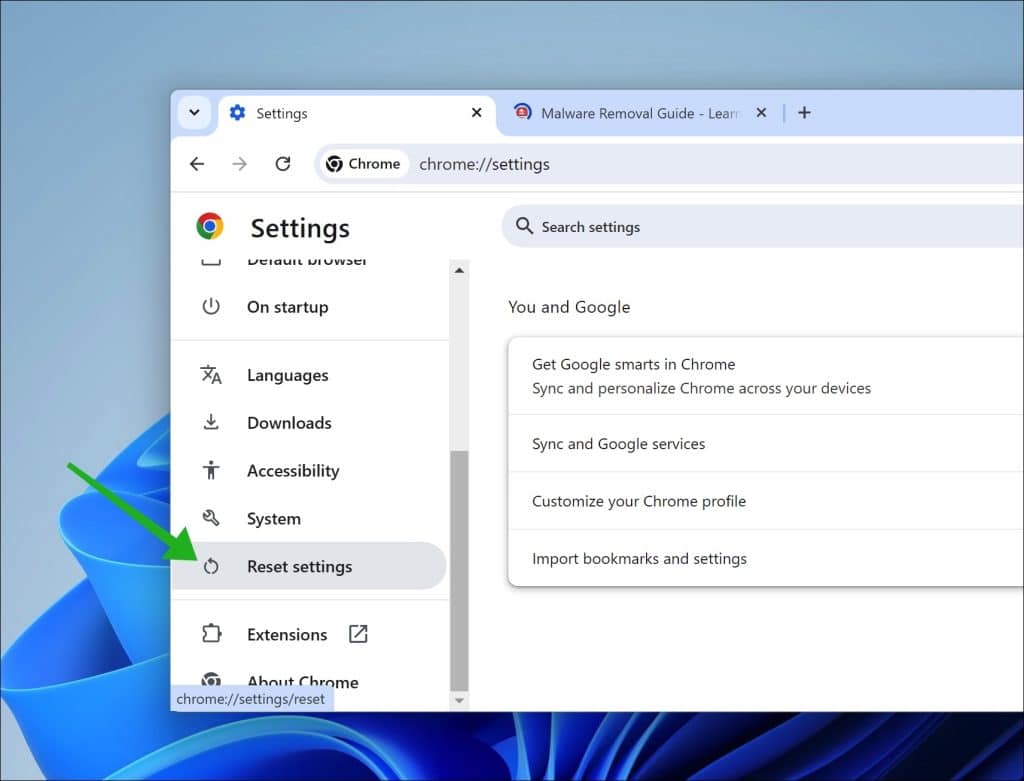
Google Chrome
- Open the menu at the top right.
- Go to Settings.
- Scroll down to Reset settings.
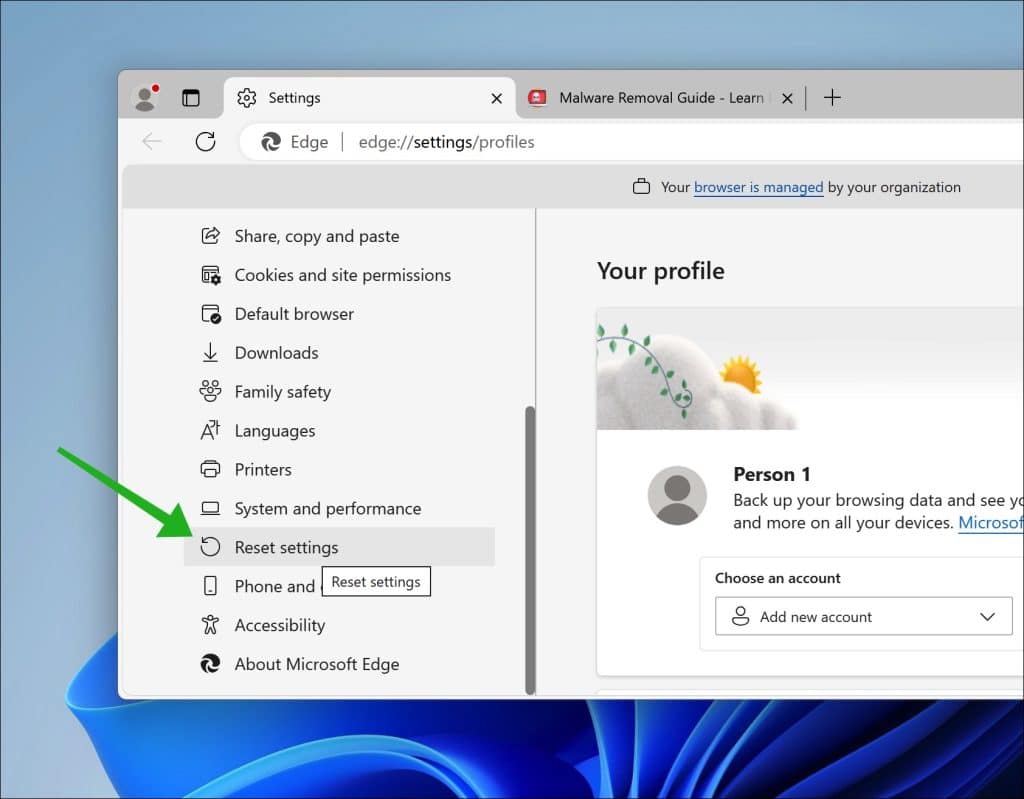
Microsoft Edge
- Open the menu at the top right.
- Go to Settings.
- Scroll down to Reset settings.
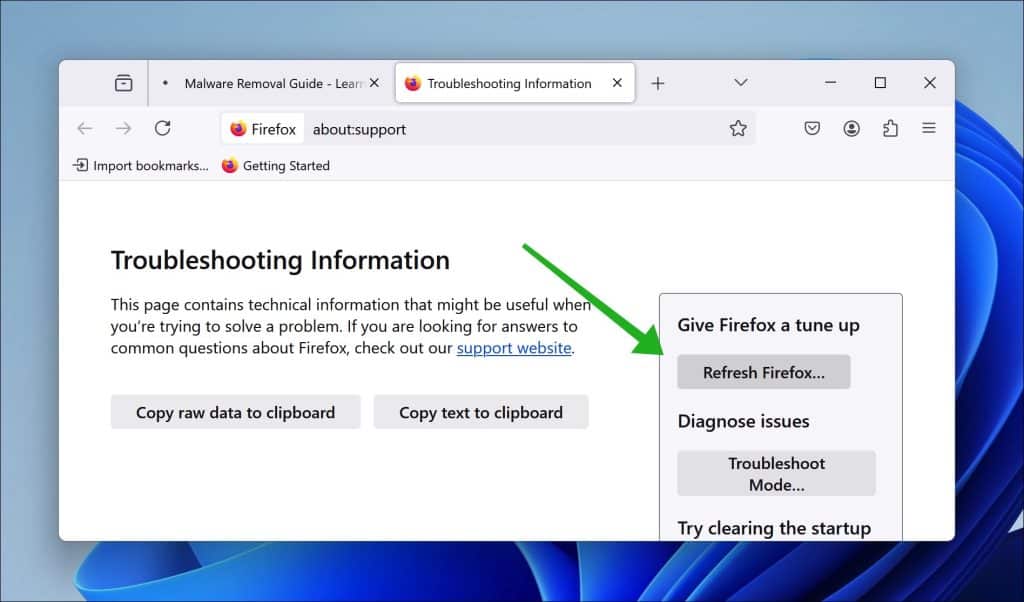
Firefox browser
- Open the menu at the top right.
- Go to Help.
- Go to More troubleshooting information.
- Click on Refresh Firefox.
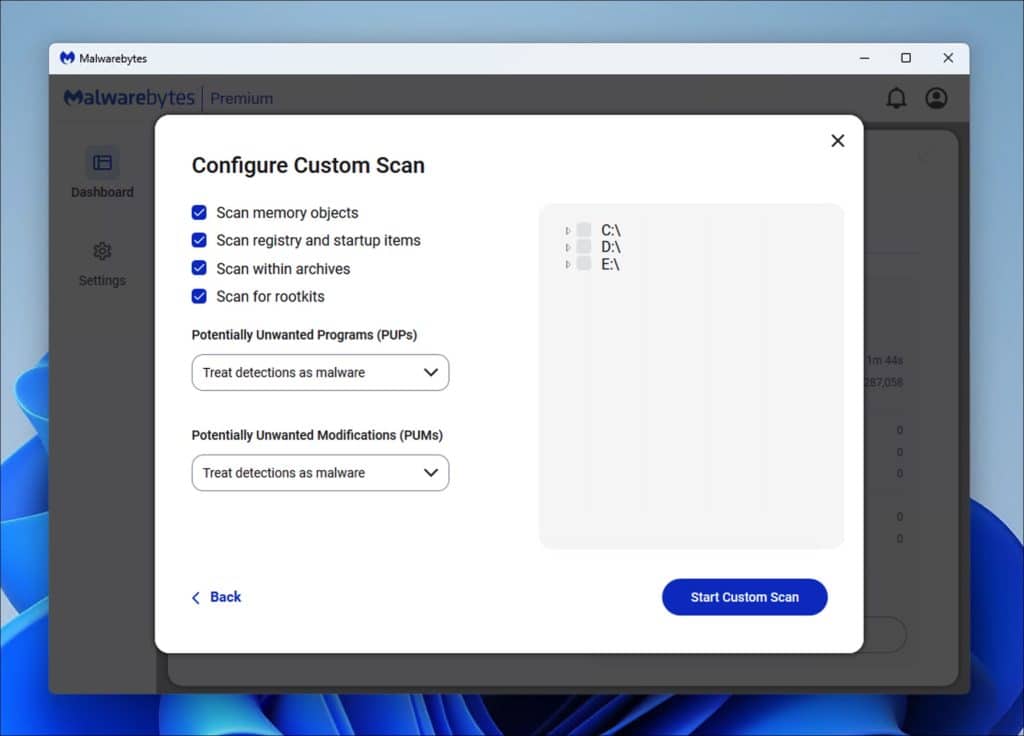
2. Download and Run Malwarebytes Anti Malware:
- Download Malwarebytes Anti Malware.
- Run a complete scan:
- Click Scan.
- Click Advanced Scan.
- Click Custom Scans.
- Select Scan for Rootkits and ensure the C: drive is ticked.
- The scan may take a while. If Malwarebytes flags any PUPS or malware, quarantine, delete, and reboot.
3. Download and Run Malwarebytes Adwcleaner:
- Download Malwarebytes Adwcleaner here.
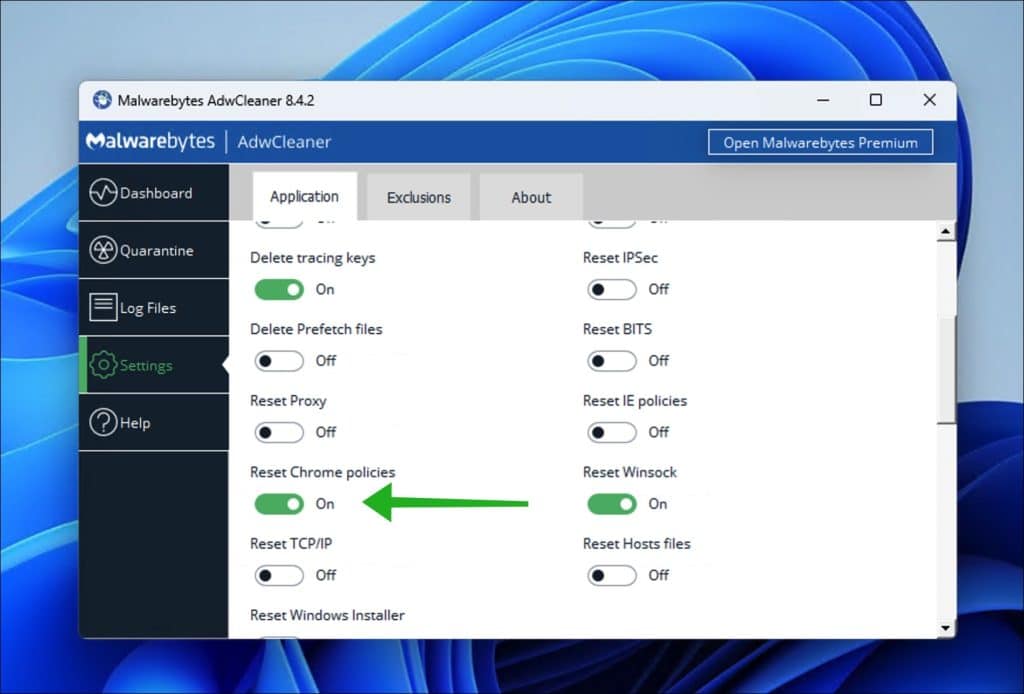
- Open the Settings and ensure Reset Chrome Policies is turned on.
- Run the scan, quarantine, and delete any PUPs or adware.
- Reboot and check Chrome Extensions again.
4. Last Resort Steps (Remove browser is managed by your organization)
Google Chrome
First method
- Open Start, type
Registry Editor, and right-click Registry Editor > Run as Administrator. Enter the Administrator password when prompted. - Open Google Chrome, navigate to
chrome://extensions, and toggle Developer Mode on. - Find the extension you wish to delete, and copy the extension ID.
- Return to Registry Editor, click Edit > Find, and paste the ID into the search box. Click ‘Find Next’.
- Wait for regedit to find the key, then right-click > Delete the registry key. This should delete the extension from root.
- Reboot the computer, and run
sfc /scannowto restore any damaged system files. The computer should now be free from any remnants of the extension.
Second Method (Only Use if the First Method Does Not Work):
- Open Start, type
Registry Editor, and right-click Registry Editor > Run as Administrator. Enter the Administrator password when prompted. - Navigate to the following keys, and right-click > Delete. Make sure to delete the Folder in the left column, not just the registry entry:
-
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Google\ChromeHKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Google\ChromeHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Google\ChromeHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Google\ChromeHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Google\UpdateHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\WOW6432Node\Google\Enrollment
-
- Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\WOW6432Node\Google\Update\ClientState\{430FD4D0-B729-4F61-AA34-91526481799D}and delete the value namedCloudManagementEnrollmentTokenfrom the registry key. - Delete the directory where Google Update stores updated cached cloud policies:
%ProgramFiles(x86)%\Google\Policies.
Microsoft Edge
- Open Start, and search for
cmd. - Right-click Command Prompt, run as administrator, and type the following command:
reg delete HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Edge /va /fRestart the Microsoft Edge browser.
5. Terminate Browser Processes:
- Close Google Chrome.
- Open Start and search for Task Manager; right-click and run Task Manager as Administrator.
- Search for the Google Update and any other Google Chrome or Google processes. Right-click and end the tasks.
6. Run System File Checker
- Close Task Manager, open Start, and search for
cmd. - Right-click Command Prompt, run as administrator, and type the following command:
sfc /scannow– This process checks for damaged system files and restores them. - Let the tool run its scan. When finished, exit CMD and reboot the computer.
- Upon reboot, open Chrome and check the extensions page. The malicious extension should now be deleted or able to be deleted. Try searching a webpage to check for any redirects.
- Run Malwarebytes again for good measure.
Your browser should be malware-free now. Thank you for reading!